quantitative study sample size|qualitative sample size justification : fabrication Sample size is a critical determinant for Linear, Passing Bablok, and Deming regression studies that are predominantly being used in method comparison studies. Sample size estimations for the Passing-Bablok and Deming method comparison studies are exemplified in Table 7 and Table . WEB1 de dez. de 2023 · A BET7K é a plataforma que atualmente oferece maior bônus de 100% no depósito. O valor final pode chegar a R$7000. Bônus: 100% até o primeiro depósito máximo de R$7000; Necessário cumprir regras e termos de uso para retirada do valor; Registre-se Aqui; Leia também: Saiba como ganhar R$5 para jogar apenas .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Santos FC | Acompanhe em tempo real as principais notícias e acontecimento sobre esportes, cultura, política e porto da Baixada Santista e região.
Sample size is a critical determinant for Linear, Passing Bablok, and Deming regression studies that are predominantly being used in method comparison studies. Sample size estimations for the Passing-Bablok and Deming method comparison studies are exemplified in Table 7 and Table .In brief, a sample size is determined by three elements: i) type I error (alpha); ii) .
The importance of an accurate sample size calculation when designing quantitative .For sample size estimation, researchers need to (1) provide information . In this review, we will discuss how important sample size calculation is for research studies and the effects of underestimation or overestimation of sample size on .
Determining an appropriate sample size is vital in drawing realistic conclusions from research findings. Although there are several widely adopted . Although sample size calculations play an essential role in health research, published research often fails to report sample size selection. This study aims to explain the . In a recent overview, Lakens (2021) listed six types of general approaches to justify sample size in quantitative empirical studies: (a) measure entire population, (b) resource .
In this overview article six approaches are discussed to justify the sample size in a quantitative empirical study: 1) collecting data from (almost) the entire population, 2) .In brief, a sample size is determined by three elements: i) type I error (alpha); ii) power of the study (1-type II error) and iii) effect size. A proper understanding of the concept of type I error .The sample size for a study needs to be estimated at the time the study is proposed; too large a sample is unnecessary and unethical, and too small a sample is unscientific and also .
The importance of an accurate sample size calculation when designing quantitative research is well documented [1–3]. Without a carefully considered calculation, results can be missed, .

small sample size qualitative research
For sample size estimation, researchers need to (1) provide information regarding the statistical analysis to be applied, (2) determine acceptable precision levels, (3) decide on . An important step when designing an empirical study is to justify the sample size that will be collected. The key aim of a sample size justification for such studies is to explain how the collected data is expected to provide valuable information given the inferential goals of the researcher. In this overview article six approaches are discussed to justify the sample size in . For quantitative projects the adequacy of the sample size must be determined before the study begins and the “size remains a constant target through the study.” ( Guetterman, 2015 ). None of these assumptions or strategies hold true for qualitative inquiry.Referring to the example for illustration purposes, the sample size calculation was calculated by using the sample size software as follows; with a study setting of equal sample size for both groups, the mean reduction is set at only 1 kg with within group standard deviation estimated at 0.8 (derived from literature, pilot study or based on a .
This free sample size calculator determines the sample size required to meet a given set of constraints. Also, learn more about population standard deviation. home . For example, if the study population involves 10 people in a room with ages ranging from 1 to 100, and one of those chosen has an age of 100, the next person chosen is more . Sample size is a term used in market research to define the number of subjects included in a survey, study, or experiment. In surveys with large populations, sample size is incredibly important. The reason for this is because it's unrealistic to get answers or results from everyone - instead, you can take a random sample of individuals that .
What is Sample Size? ‘Sample size’ is a market research term used to define the number of individuals included in research. Researchers choose their sample based on demographics, such as age, gender, or physical location.The term can be vague or specific.. For example, you may want to know what people within the 18-25 age range think of your product.
The minimum sample size is 100. Most statisticians agree that the minimum sample size to get any kind of meaningful result is 100. If your population is less than 100 then you really need to survey all of them. A good maximum sample size is usually 10% as long as it does not exceed 1000. A good maximum sample size is usually around 10% of the . YOU'VE probably been asked (or have asked) the question: How many subjects do I need for my research study? That's your sample size--the number of participants needed to achieve valid conclusions or statistical significance in quantitative research. The sample size for a study needs to be estimated at the time the study is proposed; too large a sample is unnecessary and unethical, and too small a sample is unscientific and also unethical. The necessary sample size can be calculated, using statistical software, based on certain assumptions. If n .Sample size calculation. In order to enable comparisons with some level of established statistical confidence, quantitative research needs an acceptable sample size. 2 The sample size is the most crucial factor for reliability (reproducibility) in quantitative research. It is important for a study to be powered – the likelihood of identifying a difference if it exists in reality. 2 Small .
Determining the sample size in a quantitative research study is challenging. There are certain factors to consider, and there is no easy answer. Each experiment is different, with varying degrees of certainty and expectation. Typically, there are three factors, or variables, one must know about a given study, each with a certain numerical value. Quantitative Research. Quantitative research is a type of research that collects and analyzes numerical data to test hypotheses and answer research questions.This research typically involves a large sample size and uses statistical analysis to make inferences about a population based on the data collected. Sample size considerations in research. Go to citation Crossref Google Scholar. . SAGE Quantitative Research Methods. 2011. SAGE Knowledge. Literature review . Sufficient Sample Sizes for Multilevel Modeling. Show details Hide details. Determining a good sample size for a study is always an important issue. After all, using the wrong sample size can doom your study from the start. Fortunately, power analysis can find the answer for you. Power analysis combines statistical analysis, subject-area knowledge, and your requirements to help you derive the optimal sample size for your study.
We may love our in-depth qualitative research tools, but we know the value of integrating both qual and quant methods. That’s why we have built our DIY quantitative research sample size calculator. From some basic information, .SAMPLING. Sampling can be defined as the process through which individuals or sampling units are selected from the sample frame. The sampling strategy needs to be specified in advance, given that the sampling method may affect the sample size estimation. 1,5 Without a rigorous sampling plan the estimates derived from the study may be biased (selection bias). 3
The importance of power and sample size estimation for study design and analysis. Other rules of thumb include Harris’s (1975) difference rule (accounting for model variations) based on N > 50 + 8m, where N is the sample size, 50 is the base sample, and 8m is the adjustment of sample based on the number of predictors; Kline’s (2005, 2016) sample size range for small (less than 100), medium (100–200), and large (more .Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample.The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences about a population from a sample. In practice, the sample size used in a study is usually determined based on the cost, time, or .4) Use best practice guidelines to calculate sample size. There are many established guidelines and formulas that can help you in determining the right sample size. The easiest way to define your sample size is using a sample size calculator, or you can use a manual sample size calculation if you want to test your math skills. Cochran’s .
What is Sample Size? Sample size is the number of observations or data points collected in a study. It is a crucial element in any statistical analysis because it is the foundation for drawing inferences and conclusions about a larger population.. When delving into the world of statistics, the phrase “sample size” often pops up, carrying with it the weight of your study’s credibility .Calculate power & sample size for one-sample, two-sample and k-sample experiments. Advanced power and sample size calculator online: calculate sample size for a single group, or for differences between two groups (more than two groups supported for binomial data). . Journal of Business Research 66:1261-1266. 5 Lakens D. (2014) "Observed power .
Background Estimating sample size is an integral requirement in the planning stages of quantitative studies. However, although abundant literature is available that describes techniques for . While acknowledging these limitations, this study provides some additional information that can be useful for future studies and their decisions about sample size. Specifically, this study furthers the suggestion by Bacchetti (2010) to use the sample size of other similar articles as a basis for the sample size in a new proposed study. This was .In calculating the required sample size, we need to know the characteristic of the variable of interest. Is that a continuous variable (e.g., mean) or a dichotomous variable (e.g., proportion)? In a descriptive quantitative research study, the sample size varies depending on this characteristic of the variable of interest.on one's study because the sample size is too small. This chapter includes a description of guidelines for determining sample size. Guidelines for Choosing Sample Size . Determination of sample size should begin with a review of the factors covered in Chapter 1. One should have a clear understanding of the following: • Objectives of the study:
The sample size is central in quantitative research, as the findings should be able to be generalised for the wider population.10 The data analysis can be done manually or more complex analyses performed using computer software sometimes with advice of a statistician. From this analysis, results like mode, mean, median, p value, CI and so on .
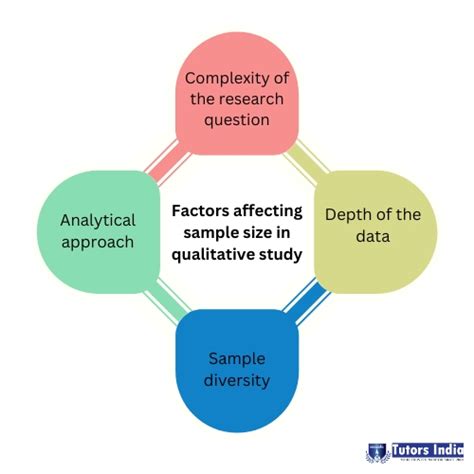
saturation sample size qualitative research
Resultado da Use 360° Images & Videos for: Spice up your campaign. Turn readers into engaged viewers. Perfect for game skyboxes, education, travel experiences and more. It's easy to drop cross-platform panoramas into mobile and web apps. Anything digital and print campaigns.
quantitative study sample size|qualitative sample size justification